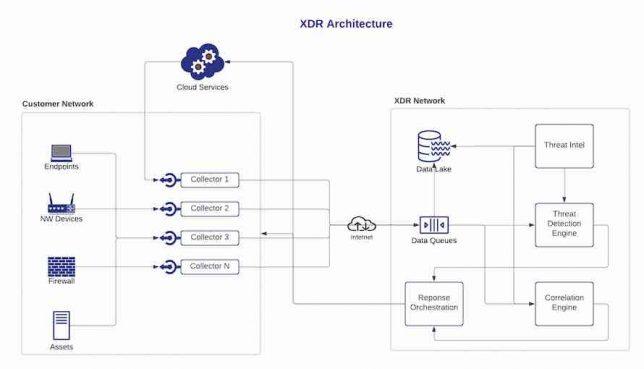
Exploring XDR Architecture: Collectors, Platform, and Response Orchestration
With the increasing number of cyber threats, organizations have been forced to adopt new strategies to combat them. One such strategy is XDR or Extended Detection and Response. XDR is a comprehensive security solution that detects and responds to threats across all endpoints, networks, and cloud environments. In this article, we will describe the architecture of an XDR product and how it works.
Architecture of an XDR Product
XDR architecture consists of three main components: collectors, XDR platform, and response orchestration. Let’s take a closer look at each of these components:
- Collectors
Collectors are responsible for collecting data from various sources, including endpoints, network devices, and cloud services. Collectors can be deployed on-premises or in the cloud, depending on the needs of the organization. They collect data in real-time and send it to the XDR platform for analysis. Collectors collect data from the following sources:
- Endpoints: Collectors can collect data from endpoints, including desktops, laptops, servers, and mobile devices. This data includes log files, system events, and network traffic.
- Network Devices: Collectors can also collect data from network devices, including routers, switches, and firewalls. This data includes network traffic and device logs.
- Cloud Services: Collectors can collect data from cloud services, including AWS, Azure, and GCP. This data includes log files, system events, and network traffic.
- XDR Platform
The XDR platform is the brain of the XDR product. It receives data from collectors and analyzes it to detect threats. The platform uses machine learning algorithms to detect anomalies and identify patterns that indicate a potential attack. It correlates data from different sources to provide a complete view of the attack and prioritize alerts based on the severity of the threat.
The XDR platform consists of the following modules:
- Data Lake: The data lake is where all the data collected by the collectors is stored. It provides a central repository for all data and allows for quick access to the data when needed.
- Threat Detection Engine: The threat detection engine is responsible for analyzing the data collected by the collectors. It uses machine learning algorithms to detect anomalies and identify patterns that indicate a potential attack.
- Correlation Engine: The correlation engine correlates data from different sources to provide a complete view of the attack. It analyzes the data to determine the scope of the attack and prioritize alerts based on the severity of the threat.
- Threat Intelligence: The threat intelligence module provides up-to-date information on the latest threats and vulnerabilities. It helps the XDR platform to detect new threats and respond quickly to emerging threats.
- Response Orchestration
The response orchestration component of an XDR product is responsible for taking action when a threat is detected. It automates the response process and can isolate infected endpoints, block malicious traffic, or perform other actions as defined by the security team.
The response orchestration component consists of the following modules:
- Automated Response: The automated response module is responsible for taking action when a threat is detected. It can isolate infected endpoints, block malicious traffic, or perform other actions as defined by the security team.
- Playbooks: Playbooks are predefined response procedures that are triggered when a threat is detected. They provide a step-by-step guide for responding to a threat and can be customized based on the needs of the organization.
- Incident Response: The incident response module provides a platform for managing incidents. It allows the security team to track the progress of an incident, assign tasks to team members, and communicate with stakeholders.
How XDR Works
The XDR product works by collecting data from different sources and analyzing it to detect threats. Here’s how it works:
- Collecting Data: Collectors are deployed to collect data from various sources, including endpoints, network devices, and cloud services. The data collected includes logs, network traffic, and endpoint activity.
- Analyzing Data: The XDR platform receives data from collectors and analyzes it using machine learning algorithms to detect anomalies and identify patterns that indicate a potential attack. The platform correlates data from different sources to provide a complete view of the attack.
- Prioritizing Alerts: The XDR platform prioritizes alerts based on the severity of the threat. It uses a risk-based approach to prioritize alerts and focuses on the most critical threats first.
- Automated Response: The response orchestration component of the XDR product automates the response process. It can isolate infected endpoints, block malicious traffic, or perform other actions as defined by the security team. The response is automated, which helps to reduce response times and minimize the impact of the attack.
Benefits of XDR
XDR provides several benefits to organizations, including:
- Comprehensive Security: XDR provides comprehensive security by detecting and responding to threats across all endpoints, networks, and cloud environments.
- Automated Response: XDR automates the response process, which helps to reduce response times and minimize the impact of the attack.
- Reduced Complexity: XDR reduces complexity by providing a single platform to manage security across all environments.
- Improved Threat Detection: XDR uses machine learning algorithms to detect anomalies and identify patterns that indicate a potential attack. This helps to improve threat detection and reduce false positives.
Conclusion
XDR is a comprehensive security solution that provides organizations with a single platform to manage security across all environments. It consists of three main components: collectors, XDR platform, and response orchestration. XDR works by collecting data from various sources, analyzing it to detect threats, and automating the response process. XDR provides several benefits, including comprehensive security, automated response, reduced complexity, and improved threat detection.